HOME(EN) Company profile CB processing CHEMIFLEX Chemical treatment ATMag HOME(JP)
Chemical Bonding processing
Forefront technology for chemically bonding resin to metal, glass, and ceramic materials without any adhesives agent
Latest data of interest [updated as necessary]
Test results on transmission loss (FCCL with Liquid Crystal Polymer and Copper Foil as Rolled)←latest data
Test results on transmission loss (copper foil with LCP)
Bright copper foil with polyimide film
Bright copper foil with LCP film
SUS for spring and polyamide type resin
Aluminum foil and CPP (Cast polypropylene film)
Stainless steel / aluminum foil and film laminate
Anodized aluminum and ABS resin
Aluminum material and epoxy prepreg
Copper and polycarbonate
・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・
You can download our free white paper on the link below
Weld bondingMajor features
●Resin is solidly bonded to glass, ceramic, and metal by chemical bonding.
●CB processing is applicable not only to thermoplastic resin, but also to epoxy or phenol-type thermosetting resin molding materials for encapsulation or sealing , and furthermore, to thermosetting sheet materials prior to curing, such as thermosetting prepreg.
●CB processing bonds and integrates resin to electronic materials such as copper foil and gold-plated parts, and ceramic substrates, anodized aluminum parts, etc.
●Weld bonding by impulse heater or laser is also applicable.
COC – SUS
PA66 – SUS
(↑please click these to watch videos.)
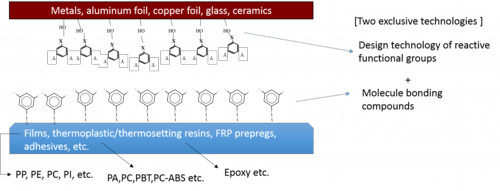
Mechanism of chemical bonding
In CB processing, the substrate (or a part) surface is chemically treated and bonded to compounds,called molecular bonding compound, which has a molecular structure to form chemical bonds to resin. Then the polymer molecular bonding compound on the substrate is chemically bound to resin molecules, so that the substrate and the resign are firmly bound and integrated.
Although CB processing performs chemical bonding like silane coupling agents, CB processing has realized a bonding strength surpasses by the silane coupling agents, CB processing has realized a bonding strength surpasses by the silane coupling agents;
1) Our own development of Si-type molecular bonding compounds,
2) Design technology of reactive functional groups by pre-processing technologies.
CB processing is a different technology from bonding resin by filling in irregularities on surface of the substrates,anchoring effect , and posses a variety of unique features.

Features of CB processing
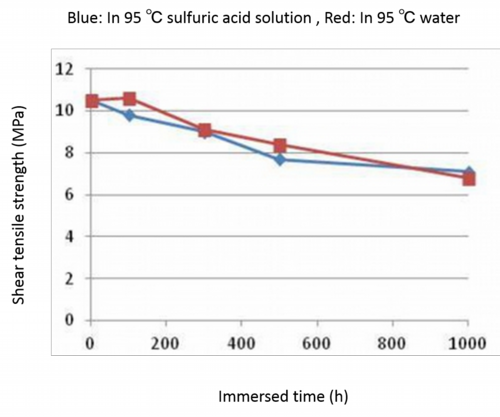
1. CB maintains the strength under severe conditions.
CB maintains the strength under severe conditions.
Durability of CB processed SUS / PBT
Bonding strength maintains after having been immersed in 95 ℃ sulfuric acid solution for1000 hours, a severe condition that PBT itself deteriorates.
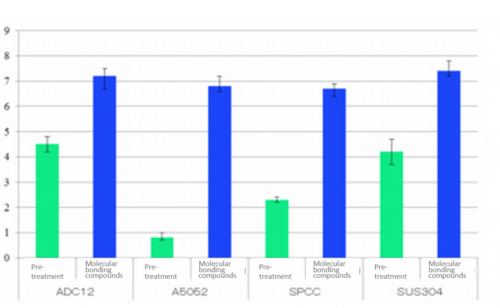
2.CB technology’s bonding strength does not depend on metal material, but on formed chemical bonding.
CB technology’s bonding strength does not depend on metal material, but on formed chemical bonding.
Tensile strength (relative value)

Molecular bonding compounds: CB technology
Pre-treatment: roughening the surface (anchoring effect)
Bonding conditions: weld bonding at 260 ℃ for 1 minute
n = 5
When resin is bonded to cold-rolled steel plates and stainless steel, rolled aluminum, and aluminum die-cast
materials, the bonding strength by roughening surfaces varies very much depending on the irregularities on surface of each metal material (anchoring effect). When the material surfaces are pre-treated by the molecular bonding compounds prior to weld bonding , bonding strength maintains almost the same regardless of the metal material.
When bonding strength between metal materials and reactive functional group is high enough, the bonding strength is governed by the structure of the molecular bond compounds and their bonding capability to the resin, so that the strength does not depend on metal materials.
3. Tensile strength by CB technology is hardly affected by decrease of hardness of the resin even when temperature is raised.
Hardly affected by decrease of hardness of the resin.

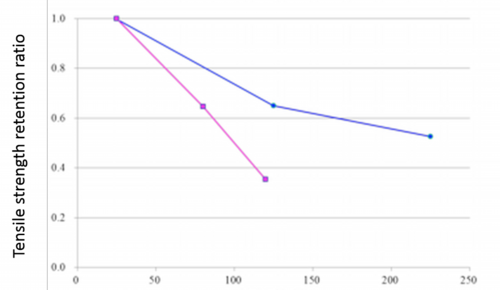
Red: Etching / Blue: CB processing
Metal: aluminum A5052
Resin: Polyamide 66, PA66 (contains glass fiber for 50%)
Test temperature / ℃
Changes in tensile strength by increasing test temperature show the difference between CB processing, which chemically binds metal and resin, and roughening surface by etching, in which the resin physically fills the irregularities on metal surface (anchor effect).
Test pieces are A5052 aluminum plate weld bonded with PA66 resin containing 60% of glass fiber.
The etched piece shows a linear decrease in bonding strength when the temperature increases. At 120 ℃, the bonding strength is lowered to less than 40% of it was at room temperature. It is considered that PA66 resin is softened by an increase in temperature, causing separation from the uneven metal surface.
In contrast, CB processed piece shows very gradual decrease; at 125 ℃, the strength retention ratio is more than 60%; even at 230 ℃ the ratio is retained more than 50%. As the interface between aluminum and PA66 resin is chemically bonded, the bonding strength maintains, resisting resin-softening.
CB processing enables to produce integrated products with excellent characteristics of metal (lightweight, high rigidity, electromagnetic shielding property, etc.) and of plastic (precise moldability, workability, flexibility, etc.) Please refer to the technical information column for more information of CB treatment.






 English articles (PDF)
English articles (PDF)